

All of its edges are the same length.Įach of the 6 faces of a cube is square-shaped because all of its edges are the same size. Marking the faces, edges and vertices as you count them is important as it can be easy to count them twice or miss one out.Ī cube has 6 faces, 12 edges and 8 vertices. You could put a sticker or piece of plasticine on each vertex as you count it.

You can mark each edge as you count it by drawing a line on each one. You can colour in each face a different colour, or write a number from 1 – 6 on each square face. When teaching this topic, it can be helpful to count the number of each property on the net before assembling it.
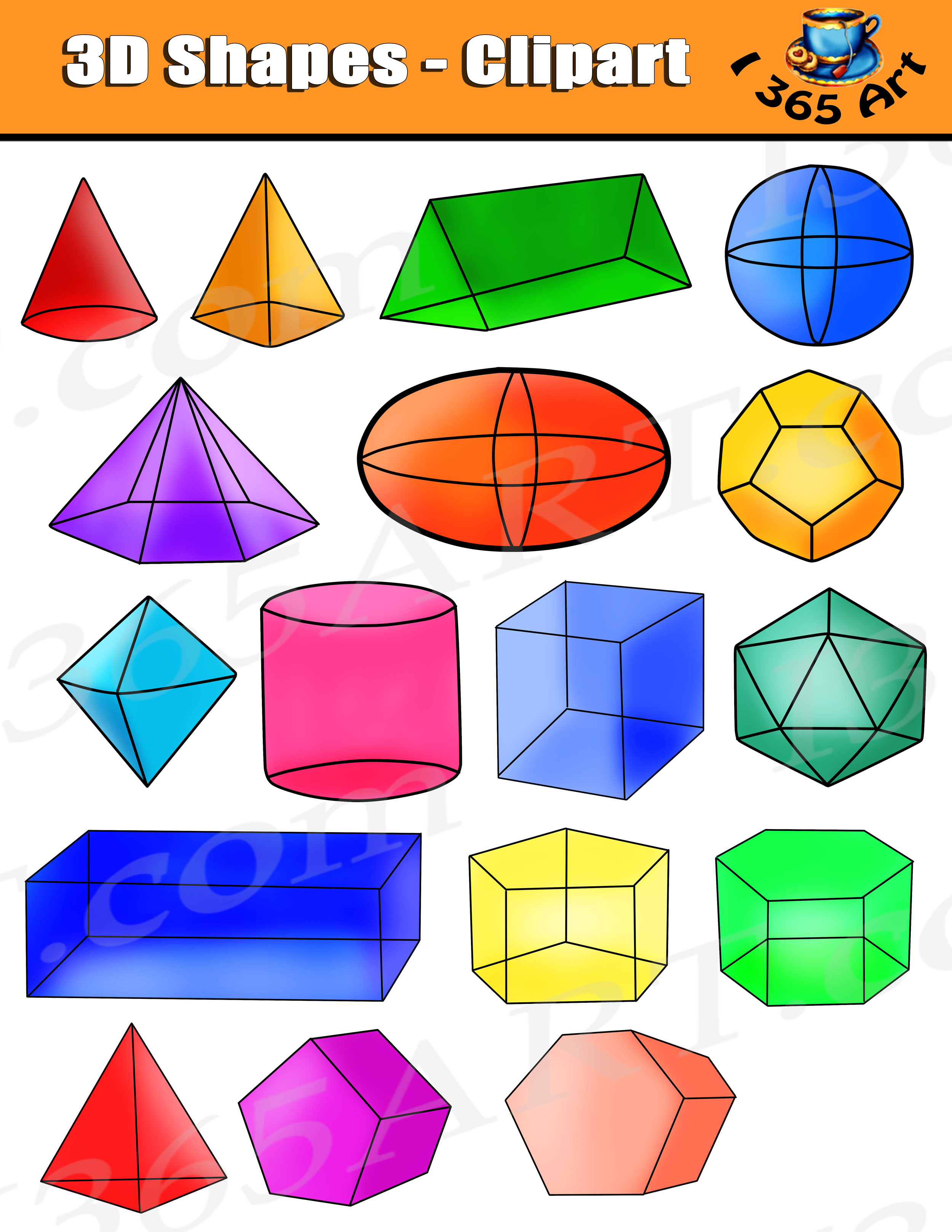
Alternatively, there are some online interactive 3D shapes in the practice section above that you can use to count the faces, edges and vertices. There are also printable nets for each 3D shape above that can be downloaded and assembled to accompany this lesson. When teaching the properties of 3D shapes, it is worth having a physical item to look at as you identify and count each property. All three dimensional shapes have the the three dimensions of length, width and depth.Ī shape is 3D if it can be picked up and held in real-life. The following table lists the number of faces, edges and vertices for some common 3D shapes:ģD is short for three-dimensional.

The poster below shows the faces, edges and vertices of 3D shapes labelled on a cube.
2d shapes and 3d shapes manual#
We can use the manual or automatic methods of creating the 2D and 3D shapes, and there are several softwares used for doing this.Conversely, for representing three dimensions, the isometric and orthographic projections are used for rendering the 3D objects. Hence we use 2D shapes in these type of plans. The plan in engineering drawing, which represents in top view, front view side view of some object are made in 2D.Square, circle, triangle, rectangle are the various 2D shapes while cube, sphere, cuboid, are the 3D shapes.On the other hand, in 3D shapes, the three axis x, y and z-axis are covered. The prior difference between the 2D and 3D shapes is that in 2D shapes only two axis are incorporated x and y-axis.These days this 3D designing is employed in the 3D printing of products. The shapes included in 3D shapes are sphere, cube, cone, cuboid, pyramid, and so on and the below-given diagram represents the 3D shapes. To illustrate the 3D in engineering, we use 2 and 3 point perspective projection and orthographic projection. The 3D shapes help in showing the depth of the object. These are used in several applications, such as in 3D animations, 3D designing of some product building, bridge, tools, 3D graphs, maps etcetera. Let’s consider a cuboidal building which is built with length, width and height is a 3D shape. The real-life examples of these shapes are buildings, balls, boxes, anything that has 3 dimensions. Definition of 3D ShapesģD shapes are solid shapes, unlike 2D shapes which are produced by combining 3 Dimensions – length, width and height. The examples of 2D shapes cover majorly the drawings made on the wall, floor tiles, covers, fabrics etcetera. There are various types of 2D shapes, among which some of them are shown below. Geological maps also made in 2 dimensions, in which we use the method of contouring to show the depth with the help of different shapes, even in oceanography also. ApplicationsĪll the parallel projections and one-point perspective projections in plans of some object are made in 2D. Now, what a 2D shape is? Before understanding the 2D shape, we must know what a 0D object is, which means there is no dimensions. In other words, the shapes that only have length and width are the 2D shapes. We can consider that the shapes which can be produced on a flat surface are said to be 2D (dimensional) Shape.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
